Developing a Strategic Plan for Medical Specialties in Oman
Dr. Moeness M. Alshishtawy
Submitted: 13 August 2007
Reviewed: 9 October 2007
Accepted: 15 November 2007
Address correspondence and reprint request to:
Dr. Moeness M. Alshishtawy, M.D., MPH, DHS, HA, PHD(PH) Senior consultant, Health Planning at MoH
Introduction
Health work is broadly defined to include not only technical skills and expertise directly responsible for creating and sustaining health but also the skills needed in support systems and the linkages that facilitate the application of technical skills. The health sector is not only labour-intensive but it also depends on a precise application of the knowledge and skills of its workforce to ensure patient safety and health.1
The crucial role of Human Resources for Health (HRH) in health systems has not been fully appreciated until recently. In Oman, the health sector has consistently experienced shortages of suitable health personnel, especially medical specialists, as one of the major constraints that might affect sustainability of the health system.2 It is now accepted that HRH is not only strategic capital but also the most important resource for the performance of the health system. It is also recognized that HRH is an integral part of the health system linked with health services provision and performance of health service providers in a relationship of mutual dependence.3
The stock of health workforce in the Sultanate has grown significantly over years. Workforce densities have improved significantly over the last two decades. At the end of 2007, the number of physicians and medical specialists per 10,000 population in the Sultanate has reached 17.9 and 6.5 respectively, compared to 9 and 2.6 in 1990.4
Medical education in Oman has developed satisfactorily when the College of Medicine & Health Sciences, Sultan Qaboos University (SQU) enrolled its first batch of 45 students for MD in 1986, thus enabling Oman to achieve increased self-reliance in physician manpower. Postgraduate medical education commenced in Oman with the establishment of the Oman Medical Specialty Board (OMSB) in 1994, as the highest supervisory body of all postgraduate medical training programs in Oman. OMSB has now been reconstituted by the Government to implement a Royal Decree (No.31/2006), enhancing its status to an independent body.
The OMSB is managed by a Board of Trustees, chaired by H.E. Minister of Health, which is responsible for overseeing the work of the board, the Executive Board and the medically specialized scientific committees that undertake the entire executive administration of the board.
Some of the functions identified for the Executive Board include implementation and monitoring of the approved training plans and programs; establishment of the specifications, criteria and conditions required for the accreditation of hospitals and health centers utilized for specialized medical training, management and organization of the training and examinations affairs, and proposing conditions for admission to training programs, etc. In order to achieve these functions in a constructive and scientific way, the OMSB Executive Board thought of formulating a policy and a visionary plan for medical specialties in Oman in the light of given resource constraints. This comes in line with the intention of OMSB of preparing Five Year developmental plans in the near future in accordance with the policy of the Government of Oman. So, it has been decided to embark on 2 consecutive medium term plans in the preparatory phase before being indulged into the official Five-Year plans. According to this arrangement, it was decided that the first proposed plan will cover a period of three years (2009-2011) and the second plan will cover a period of four years (2012-2015). Accordingly, the first official Five-Year developmental plan for the OMSB should be the third one covering the period (2016-2020).
The Ten Steps for Developing OMSB Strategic Plan (2009-2011)
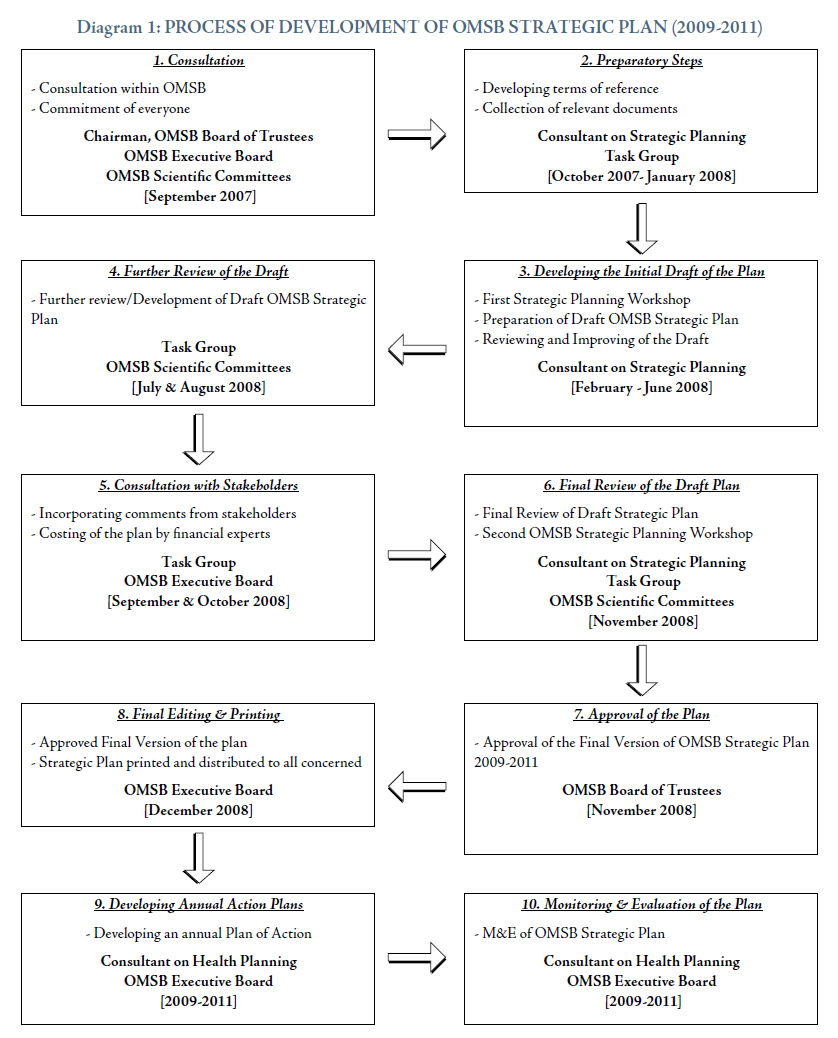
As described in figure 1, the process for Developing OMSB Strategic Plan is further explained below:
Consultation
The first stage is consultation within OMSB Executive Board members and chairpersons of the OMSB Scientific Committees. The OMSB Executive Board formed a Task force which included representatives from the OMSB and other institutions (e.g. Ministry of Health “MoH”, Sultan Qaboos University “SQU”, etc.) and selected a focal point for the process, i.e. Consultant on Strategic Planning. The OMSB Board of Trustees has provided guidance for the framework of the process.
Preparatory steps
This stage included developing the terms of reference for the Task force. All relevant documents were collected. These included policies affecting OMSB functions, Local and international experts’ reports, guidelines for medical specialties development, MoH Policy statement on HRH; MoH Policy statement on Continuing Professional Education; MoH policy on HRH and MoH 7th Five-Year Plan for Health Development (2006-2010). These provided the background for the SWOT analysis of medical specialties in Oman.
Developing the initial draft of the plan
The third stage of the process was accomplished by conducting the First Strategic Planning Workshop during the period 11-13 February 2008. The workshop, organized by OMSB Executive Board, aimed at producing a draft Strategic Plan for Medical Specialties in Oman for the period (2009-2011), and was attended by approximately 110 participants.
The process for the development of the strategic plan included the following steps:
-
Situation Analysis of Medical Specialties in Oman using SWOT Analysis.
-
Development of Mission, Values & and Vision for OMSB.
-
Development of defined Goals.
-
Development of Objectives for the period of 2009-2011.
-
Development of Strategies that are linked to resource allocation.
-
Development of indicators for monitoring progress.
-
Development of Implementation Plan (Outline of activities, resources, accountability, and timelines - usually annual at operational level). This step will be carried out at the beginning of each cycle of the three years of the plan.
The final product of the workshop was a draft plan that was reviewed, elaborated and improved by the Consultant on Health Planning.
Further review of the draft
The fourth stage consists of presenting the reviewed & improved plan to the members of the Task force and OMSB Scientific Committees for review. Once this is accomplished, the complete document will be sent to all concerned inside and outside OMSB.
Consultation with stakeholders
The Task force will incorporate comments/suggestions received from stakeholders and submit the final draft to the OMSB Executive Board. Costing of the plan by financial experts will be done at this stage.
Final review of the draft plan
Final review and improvement of the plan draft will be done in a two- day workshop that will be organized for that purpose. Invitations will be sent to the same attendants of the First Strategic Planning Workshop. Panel discussions will be organized during the workshop with the inVolvement of international experts from different related fields. Comments and suggestions raised and discussed during the workshop, where appropriate, will be incorporated into the Strategic Plan.
Approval of the plan: The sixth stage will be the approval of the plan by the OMSB Board of Trustees followed by the allocation of resources to implement the plan.
Final editing and printing: The seventh stage will be printing a well-edited plan (originally in English then being translated into Arabic) and its distribution to all concerned.
Developing annual action plan:
Since the OMSB Strategic Plan is formulated for three years, an annual action plan will be developed for feasibility as well as to address resource implications. The OMSB Executive Board will coordinate with the OMSB Board of Trustees to implement these plans. The OMSB Board of Trustees will provide leadership, finance and advise to all those inVolved to ensure the timely and successful implementation of action plans.
Monitoring and evaluation of the plan: The implementation of the plan will be monitored by the OMSB through the Executive Board. A methodology for Monitoring & Evaluation (M&E) will be suggested by the Consultant on Strategic Planning. A multidisciplinary coordination committee for monitoring the implementation of the plan will be established. The terms of reference of the committee and the frequency of its sessions will be decided. This process will include extracting the M&E indicators that are part of the plan. Starting from 2009, an annual M&E workshop will be organized for that purpose.
Some Features of the OMSB Strategic Plan (2009-2011)
The strategic plan is developed in order to operationalize the OMSB Policy and to determine what actions need to be taken to reach the goals set down in the policy document. In other words, the plan specifies and sets objectives with expected results by providing sufficient details of what is to be produced or achieved, why and at what cost. OMSB Strategic Plan does the mapping for three years (2009-2011) and contains a detailed situation analysis of medical specialties in Oman, the issues, the objectives and the strategies to solve the identified problems and challenges during the given period.
The format of OMSB Strategic Plan is country-specific and it contains the major elements: Mission, Values, Vision, Goals, Objectives, and Strategies. These are outlined as follows:
Mission: To provide a teaching, learning and research environment which fosters excellence in postgraduate medical education, training, assessment and accreditation throughout the Sultanate of Oman. Through this, the healthcare and health of patients and the Omani community can be improved.
Values: The Oman Medical Specialty Board (OMSB) values accountability, affordability, accessibility, consistency, commitment, quality, efficiency, ethics and loyalty. These values and aspirations are given effect through a distinctive set of organizational attributes which include team work, decentralization, stakeholder consultation and community participation to form productive and sustainable partnerships. Transparency and credibility in engaging with the community, in education, training and research, enable the OMSB to make a positive social, economic and environmental impact which benefits the inhabitants of the Sultanate of Oman.
Vision: OMSB vision is to develop sufficient numbers of medical specialists in various fields in medicine, as needed nationally, to deliver excellent health care of international standards, to the people of Oman with competence and compassion and to place Oman in the forefront of postgraduate education and training in the region.
Domains, Strategic Goals & Objectives
Domain: Education and Training
Goal 1: To participate in developing specialists in different fields of medicine with up-to-date knowledge, critical thinking skills and evidence based practice.
Objectives:
To attract the best trainees.
To organize the intake of residents according to the country’s needs.
To develop the sub-specialty to the acceptable level/status.
To improve community awareness of OMSB program.
To restructure curricula towards student centered/self learning.
To promote evidence based practice.
Domain: Functioning Programs
Goal 2: To develop, review, and supervise postgraduate medical specialty programs for doctors and other health professionals consistent with changing needs of the health care system in Oman and international trends.
Objectives:
To achieve good supervision of Residents.
To maintain regular & periodic evaluation of rotation by the residents.
To review periodically the curriculum in order to develop up-to-date curricula based on identified needs.
To improve the communication between different programs.
To improve communication between residents and program directors.
To enhance leadership and management of OMSB programs.
Domain: Continuing Medical Education (CME)
Goal 3: To update the knowledge of health care professionals and maintaining their competencies in their specialties.
Objectives:
To create a sustainable and healthy learning environment in OMSB facilities and allied institutions.
To set up/organize continuing medical education programs/activities for residents in different health specialties.
Domain: Quality Assurance and Improvement (QA&I)
Goal 4: To implement a quality assurance system for postgraduate medical education and training that is benchmarked against national and international standards.
Objectives:
To develop a QA&I system for OMSB programs.
To build the capabilities and empower the QA&I Committee for implementing the QA process.
To ensure all programs are prepared for Quality Audit by OMSB Accreditation Committee.
OMSB residency programs to be accredited by OMSB.
Domain: Infrastructure and Resources
Goal 5: To provide advanced educational resources to promote an innovative teaching/learning environment.
Objectives:
To upgrade training centers especially in the regions.
To ensure the efficient and effective use of educational resources.
To conduct a needs assessment study for learning resources of all programs.
To provide necessary resources in a phased manner according to the needs of each program.
To set up a system to ensure provision and maintenance of the new selected technology.
To develop staff & residents knowledge and skills to use the identified technologies.
To ensure sufficient physical space for the needs of all educational activities.
To enhance student records system.
Domain: Teaching Workforce
Goal 6: To develop and retain a highly qualified teaching workforce comprising appropriately qualified staff to meet the growing needs of residents in accord with national and international standards of medical education.
Objectives:
To recruit and maintain appropriate number of highly qualified trainers and support staff for each program.
To provide a coordinated approach to career and professional development for all staff members.
To develop career structure and job descriptions for all categories of trainers in OMSB programs.
To establish a consistent and relevant internal performance appraisal system.
Domain: Regional and International Relations
Goal 7: To create an environment of constructive coordination and cooperation with other professional health councils, medical organizations and associations and other health professional colleges within or outside the Sultanate (Gulf Region, Middle East or internationally).
Objectives:
To have affiliations for each specialty with benchmark institutions regionally or internationally.
OMSB residents will have opportunities for fellowship positions regionally or internationally.
Domain: Research
Goal 8: To promote and increase research activities of staff and residents, with the aim of strengthening the quality of educational programs and improving health of individuals and communities.
Objectives:
To develop a research culture at program level.
To enhance research capacity and capabilities of staff and residents.
Conclusion
The process and the steps needed for the development of OMSB Strategic and Action Plans for Medical Specialties in Oman have been detailed... Comments and suggestions on the process and the proposed plan are welcomed and can be submitted directly to OMSB.
The vision, values and principles of OMSB include realistic expectations and quality considerations, as well as ethics. The content of the strategy document reflects what the country’s aspirations are in addressing the major issues and challenges of medical specialists’ development and management. These aspirations should always be elaborated as a key resource for the achievement of high quality health care and service delivery.
References
-
WHO. The People Who Work for Our Health: Placing Health Workers at the Heart of Health Services Delivery. Division of Health Systems and Services Development, Regional Office for Africa, 2003.
-
Ministry of Health, Oman. The 7th Five-Year Plan for Health Development (2006-2010).The National Strategic Plan, 2006.
-
WHO. Human Resources for Health: Developing Policy Options for Change. Discussion Paper. Draft. Geneva, 2002.
-
Ministry of Health, Oman. Annual Health Report 2007, Directorate General of Planning, Department of Information and Statistics, 2008.